
This shortcode is only available on vendor store pages.

صيدلية البعادي البيطرية

This shortcode is only available on vendor store pages.
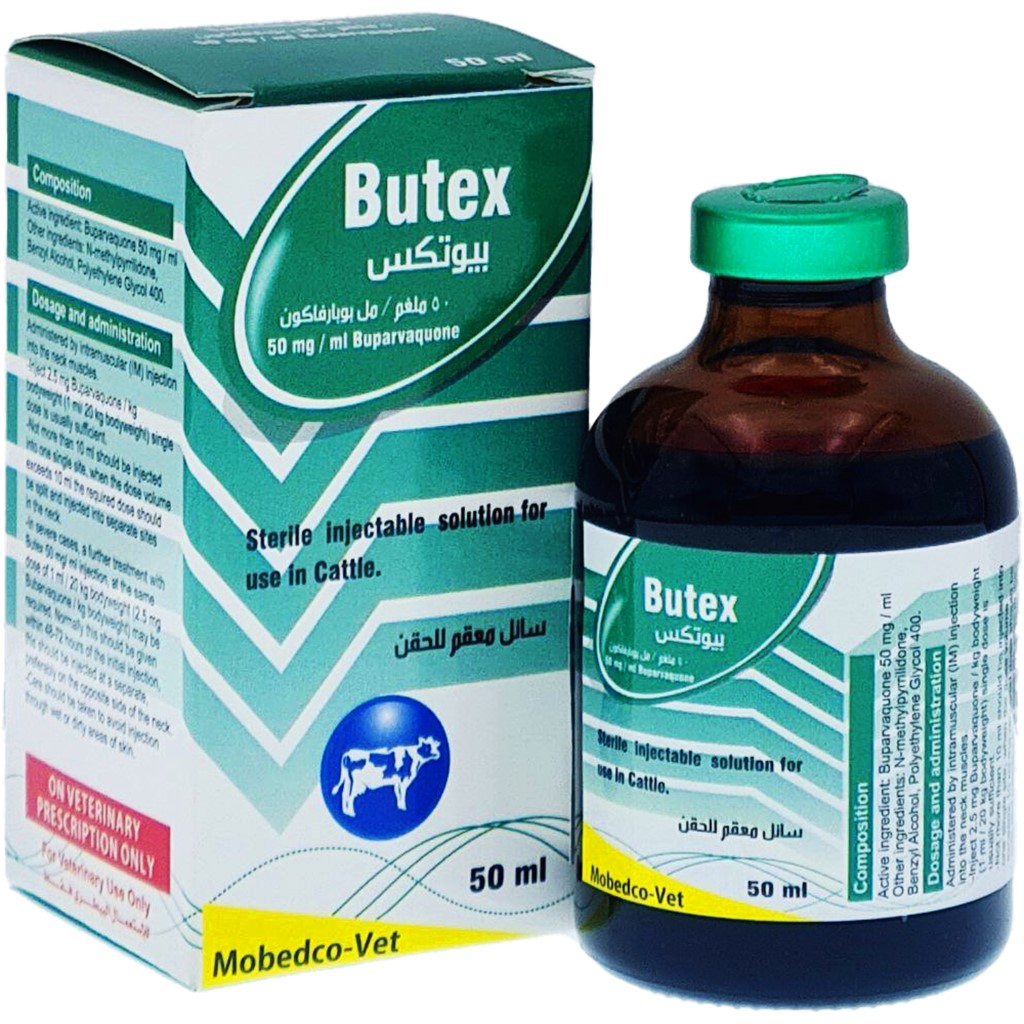
BUTEX | BUPRAVAQUOE | Treatment OF theileriosis in cattle
for veterinary injection with prescription
Butex anti protozoal contains Buparvaquone for treatment of Theileriosis in cattle read more about it
COMPOSITION:
BUTEX contain:
Buparvaquone ………………….. 50mg/ml
N-methyl pyrrolidone-Benzyl Alcohol
Properties::
-Buparvaquone is a Hydroxynapthaquone used for the treatment of Theileriosis in cattle.
-Napthaquinones are thought to interfere with electron transport chain mechanism within mitochondria.
-Napthaquinones have Long plasma half-life: at least 7 days.
INDICATION:
BUTEX used for the treatment of theileriosis in cattle
Contraindications:
-Intravenous and subcutaneous injections are contraindicated.
DOSAGE &Administration:
administrated by IM injection in neck muscle
-Inject 2.5mg /Kg body weight (1ml / 20 kg bodyweight) single dose is usually sufficient.
-Not more than 10 ml should be injected into one single site, when the dose-volume exceeds 10 ml the required dose should be split and injected into separate sites in the neck.
– In severe cases, further treatment with Butex 50 mg/ml injection, at the same dose of 1ml Butex / 20 kg body weight (2.5mg Buparvaquone/ kg body weight) may be required, normally this should be given within 48-72 hrs of the initial injection, this should be injected at a separate, preferably on the opposite side of the neck.
-Care should be taken to avoid injection through wet or dirty areas of skin.
Withdrawal period:
– Meat : 42 days.
. Milk 48 hours
Side effects:
-Localized, painless, oedematous swelling may occasionally be observed at the injection site with Butex
Precautions :
-In cases of severe theileriosis relapses may occur requiring further treatment with Butex.
-Recovered animals will develop homologous immunity.
-However any subsequent infections with antigenically unrelated species or strains of Theileria may require further treatment
– In the presence of an outbreak of theileriosis, prompt dipping or spraying of all animals at risk must be an integral part of the disease control procedure.
-Care should be taken to ensure that an approved acaricide is used, at the correct concentration and that all animals are dipped or sprayed. Sick animals should be hand sprayed, causing as little stress as possible.
Dead animals should be hand sprayed, as any ticks which leave them may pass on the infection.
-Attention should be given to the possibility of other tick-borne infections.
-Supportive antibacterial chemotherapy may be needed for the control of secondary infection.
-Anaemia is a frequent characteristic of Theileria spp infections, particularly those caused by T.annulata, T.sergenti, and T.Mutans, Consideration should therefore be given to the need to give supportive therapy for this Anaemia.
-Theileriosis has severe depressant effects on the immune system. Therefore, it is recommended that any vaccinations be delayed until the animal has recovered.
Storage:
Store in a dark and dry place below 25°C.
Vendor Information
- Store Name: صيدلية البعادي البيطرية
- Vendor: صيدلية البعادي البيطرية
- Address: المملكة العربية السعودية
- No ratings found yet!
Metacam | Anti-inflammatory | for cows and horses
Sold by صيدلية البعادي البيطريةIMIDOL | Imidocarb Injection | Drug for babesiosis, anaplasmosis
Sold by صيدلية البعادي البيطريةBUTADIN | Phenylbutazon | anti inflammatory drug | for horses
Sold by صيدلية البعادي البيطريةOLIGO SAV | VITAMINS, MINERALS & AMINO ACIDS INJECTION | FOR ANIMALS
Sold by صيدلية البعادي البيطريةgamma plex | Vitamins, minerals and amino acids| for veterinary use
Sold by صيدلية البعادي البيطريةRelated Products
-
Butalex | Buparvaquone |veterinary treatment of Theileriosis
Sold by الحصن الحصين البيطريةRated 0 out of 5350 ر.س









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.